Workaholism, causes, symptoms and treatment
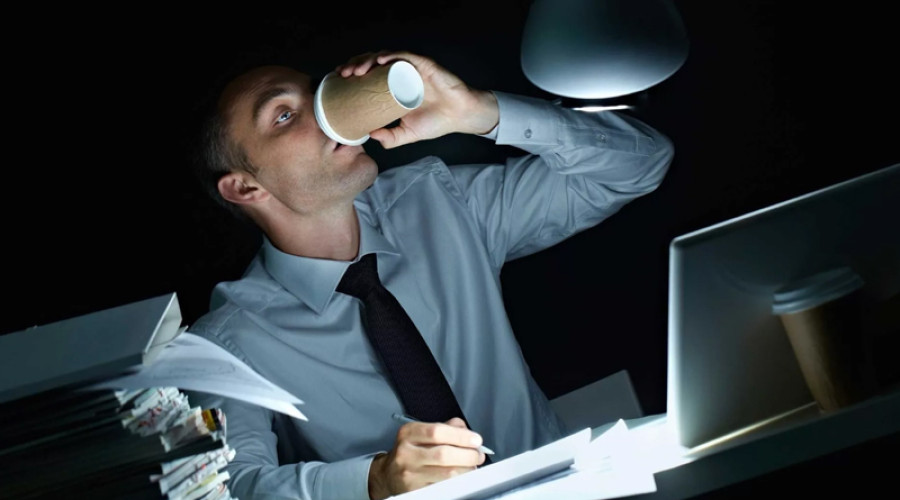

Workaholism, or pathological dependence on work, has become a common problem in modern society. People suffering from workaholism devote excessive amounts of time and energy to work, often at the expense of personal time and health. Although hard work is generally considered a positive trait, excessive obsession with work can lead to serious health issues, relationship problems, and a diminished quality of life.
How Workaholism Manifests
Workaholism can be recognized by the following signs:
- The person considers work the highest priority in their life.
- The workaholic cannot consciously control their workload or decide to stop working.
- The need to constantly increase working hours to feel a sense of importance.
- Workaholics often feel guilt and anxiety if they do not complete everything planned.
- The person cannot say "no" to new tasks and is reluctant to ask for help.
- Neglecting health and personal relationships in favor of work.
Causes of Workaholism
Personal Factors
- Perfectionism — the drive for perfection in everything a person does can lead them to work without rest;
- Low self-esteem: people with low self-esteem may seek recognition and self-assertion through professional achievements.
Social Factors
- Cultural expectations — in some cultures, workaholism is encouraged and seen as a sign of success;
- Work environment — high expectations and demands at work can drive people to overwork.
Economic Factors
- Financial needs — the necessity to earn more money to support the family may compel a person to work overtime;
- Career ambitions — the drive for career advancement may push someone to work without rest.
Symptoms of Workaholism
- Constant thoughts about work;
- Neglect of personal life and rest;
- Difficulties delegating tasks;
- Guilt when not working;
- Using work as a way to avoid problems;
- Stress and anxiety related to work;
- Neglect of health for the sake of work;
Who is Susceptible to Workaholism
Workaholism is most commonly developed in people with specific risk factors:
- Low motivation, difficulty achieving personal goals;
- Difficulty controlling one’s behavior;
- Constant need for excitement, difficulty handling boredom;
- Cultural and familial norms that encourage self-sacrificing work.
Why People Become Workaholics
Psychological reasons for workaholism include:
- The need for love and approval, where a person seeks to earn good regard through excessive work;
- The need for social recognition, where self-esteem depends on others' opinions;
- The need for a partner, where work replaces personal relationships as a way to avoid loneliness;
- The need for constraints, where work helps avoid responsibility and making important decisions;
- The need for superiority, where a person feels superior to others through constant work.
Treating Workaholism with Psychotherapy
Mental health professionals view workaholism as a form of addiction requiring professional intervention. Effective treatment is only possible if the person acknowledges the presence of the problem. A key step in overcoming workaholism is consulting a qualified psychologist who can help identify and address the underlying causes of addictive behavior.
The therapeutic approach to treating workaholism usually includes both individual and group psychotherapy sessions, which have shown high effectiveness. It is worth noting that women suffering from workaholism may face a longer recovery process.
For women seeking to overcome workaholism, the following strategy is recommended:
- Regular consultations with a psychologist and participation in specialized training.
- Planning mandatory rest after completing work tasks, such as going to the movies, spa treatments, or nature outings.
- Openness to social interactions, including accepting invitations for dates.
- Finding and developing hobbies unrelated to work.
This comprehensive approach aims to restore balance between professional and personal life, promoting overall improvement in quality of life and emotional well-being.
If you are experiencing signs of workaholism, our portal’s specialists are ready to offer professional help and support. Our psychologists can help you develop individual strategies to overcome workaholism and restore balance between work and personal life.