Psychologist's help with oncology
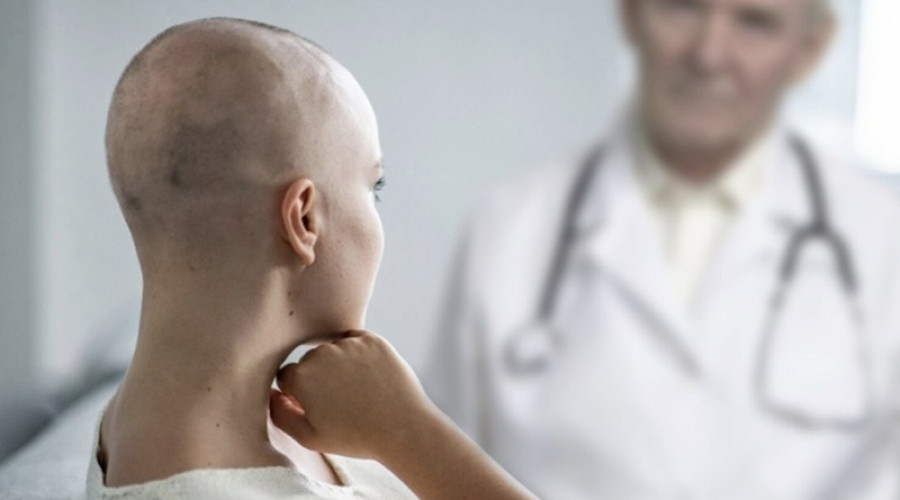
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, diagnosis, and treatment of malignant tumors. These tumors, known as cancer, can occur in any organ or tissue in the body. Oncological diseases are among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. However, modern methods of cancer diagnosis and treatment allow many patients to achieve lasting remission and significantly improve their quality of life.
Causes of Cancer
Cancer is a complex disease that can develop due to the influence of multiple factors. Malignant tumors arise from changes in the DNA of cells that disrupt normal processes of growth and division. The causes of such changes can be both external and internal.
Major factors contributing to the development of cancer:
-
Genetic Predisposition: Inherited mutations can increase the risk of certain types of cancer. For example, mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are linked to a higher likelihood of breast and ovarian cancer.
-
Harmful Habits: Smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use negatively affect body cells, increasing the risk of malignant tumors.
-
Environmental Factors: Pollution, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, radiation, and toxic chemicals can also cause mutations in cells.
-
Infections: Some viruses, such as the human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis B virus, can trigger specific types of cancer.
-
Diet and Lifestyle: Poor nutrition, obesity, and lack of physical activity are associated with a higher risk of cancer.
Types of Oncological Diseases
Oncology encompasses a wide range of diseases that may present with various symptoms and require different approaches to treatment. The most common types of cancer include:
-
Lung Cancer: The most common and deadly type of cancer, often associated with smoking and exposure to harmful chemicals.
-
Breast Cancer: One of the most common cancers in women, although it can also occur in men.
-
Prostate Cancer: The most prevalent cancer in men, especially in older age groups.
-
Colorectal Cancer: Often linked to diet and heredity.
-
Skin Cancer: Can be caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
-
Leukemia: Cancer of the blood-forming system, most commonly affecting children and adolescents.
Diagnosis of Oncological Diseases
Early diagnosis of cancer is a crucial factor for successful treatment. Modern diagnostic methods allow for the detection of oncological diseases at early stages when treatment is most effective.
Key diagnostic methods include:
-
Laboratory Tests: Blood and urine tests can detect the presence of cancer cells and markers indicating oncological disease.
-
Imaging Studies: CT scans, MRI, ultrasound, and X-rays allow for the visualization of tumors and assessment of their size and spread.
-
Biopsy: Sampling tissue for histological examination helps determine the presence of malignant cells and the tumor type.
-
Endoscopy: Allows for the examination of internal organs and collection of tissue samples for analysis.
Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatment depends on the type, stage, and location of the tumor, as well as the patient's overall health. The most effective approach typically involves a combination of several treatment methods.
Main methods of cancer treatment:
-
Surgery: Removal of the tumor and surrounding tissues is the most common method for treating early-stage cancer.
-
Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells.
-
Chemotherapy: Involves drugs that kill cancer cells or slow their growth.
-
Immunotherapy: Uses drugs that help the body's immune system fight cancer.
-
Hormone Therapy: Applied for hormone-dependent cancers such as breast and prostate cancer.
-
Targeted Therapy: Uses drugs that specifically target certain molecules in cancer cells, preventing their growth and division.
Support and Rehabilitation
Oncological diseases significantly impact not only physical health but also psychological well-being. Psychological support may be necessary to deal with anxiety, depression, and other psychological issues that can arise during treatment. Psychologists help patients and their families cope with the emotional stress that comes with a cancer diagnosis.
Role of psychological support:
-
Emotional Support: Psychologists assist patients and their families in dealing with the emotional experiences that occur during treatment.
-
Developing Coping Strategies: Psychologists teach patients stress management skills and help develop positive thinking strategies.
-
Improving Quality of Life: Psychological support helps patients adapt to new life conditions and improve their quality of life during and after treatment.
Oncological diseases are a significant challenge for modern society, but early diagnosis and modern treatment methods make it possible to successfully fight cancer and improve patients' quality of life. If you are faced with this problem, do not delay seeking medical and psychological help. Submit a request on our website, and our specialists will assist you in overcoming all stages of treatment, providing the necessary support and care. Remember, timely help and support can play a decisive role in the fight against cancer.