Psychologist's help with insomnia
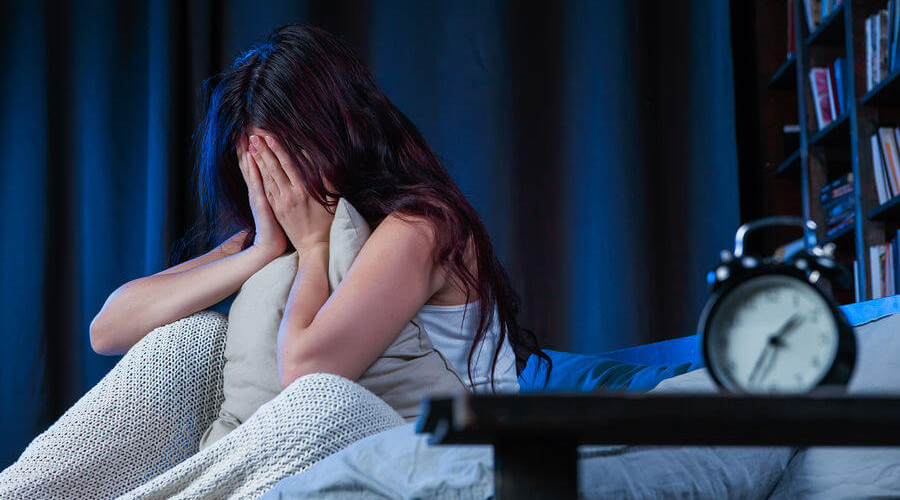

Insomnia: How to Cope with Sleep Disorders
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep. In today's world, the issue of insomnia is becoming increasingly relevant, as people face elevated stress levels, lifestyle changes, and constant busyness. The impact of insomnia on the quality of life is significant: it can lead to fatigue, decreased productivity, and even serious health problems.
Causes of Insomnia
Insomnia can arise from various causes, ranging from physical to psychological factors. The main causes of insomnia include:
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional tension caused by stress at work, study, or personal life can significantly affect sleep quality.
- Depression: Psychological disorders, such as depression, are often associated with sleep disturbances, making insomnia a common symptom of this condition.
- Poor Sleep Habits: Late-night sleeping, irregular sleep schedules, watching TV, or using gadgets before bedtime can negatively impact falling asleep and sleep quality.
- Illnesses: Some physical conditions, such as chronic pain, breathing problems, or hormonal disorders, can cause insomnia.
- Medications: Some drugs, especially those stimulating or depressing the central nervous system, may disrupt sleep.
Types of Insomnia
Insomnia is classified according to various parameters, including its duration and nature of manifestation:
-
Short-term Insomnia: Can last from several nights to several weeks. It is most often caused by stress or changes in usual lifestyle.
-
Chronic Insomnia: Lasts at least three nights a week for three months or more. It often requires a comprehensive approach in treatment, including psychotherapy and lifestyle changes.
-
Primary Insomnia: Manifests as an independent disorder without apparent causes, unlike secondary insomnia, which is a symptom of another disease or condition.
Impact of Insomnia on Health
Long-term insomnia can significantly affect physical and mental health:
- Fatigue and Energy Loss: Lack of sleep leads to constant fatigue and a decrease in energy levels, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks.
- Problems with Concentration and Memory: Sleep disturbances affect cognitive functions, impairing attention, memory, and decision-making ability.
- Increased Risk of Serious Diseases: Long-term insomnia may increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and depression.
- Emotional Instability: Chronic insomnia can lead to irritability, anxiety, and depression, exacerbating psycho-emotional problems.
Methods of Treating Insomnia
The approach to treating insomnia depends on its cause and severity. The most effective methods include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): This is the first choice in treating chronic insomnia. CBT-I helps change negative thoughts and habits associated with sleep and adopt new, healthier sleep practices.
- Pharmacotherapy: Used in the short term to stabilize sleep, especially in severe manifestations of insomnia. Medications for insomnia include sedatives, antidepressants, and melatonin.
- Sleep Hygiene: Adopting sleep hygiene rules, such as creating a comfortable sleeping environment, avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bedtime, regular physical exercises, and setting a regular sleep schedule, can significantly improve sleep quality.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices like meditation, breathing exercises, and yoga can help reduce stress levels and improve sleep.
Conclusion
Insomnia is a serious problem that requires a careful approach to diagnosis and treatment. If you or your loved ones experience sleep problems, it is important to consult specialists. On our portal, you can receive qualified assistance from experienced psychologists and psychotherapists who will help you cope with insomnia and improve your quality of life.
Research and Evidence
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials - Study on the effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy in treating insomnia.
- The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Cognitive Performance: A Meta-Analysis - Analysis of the impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive functions.